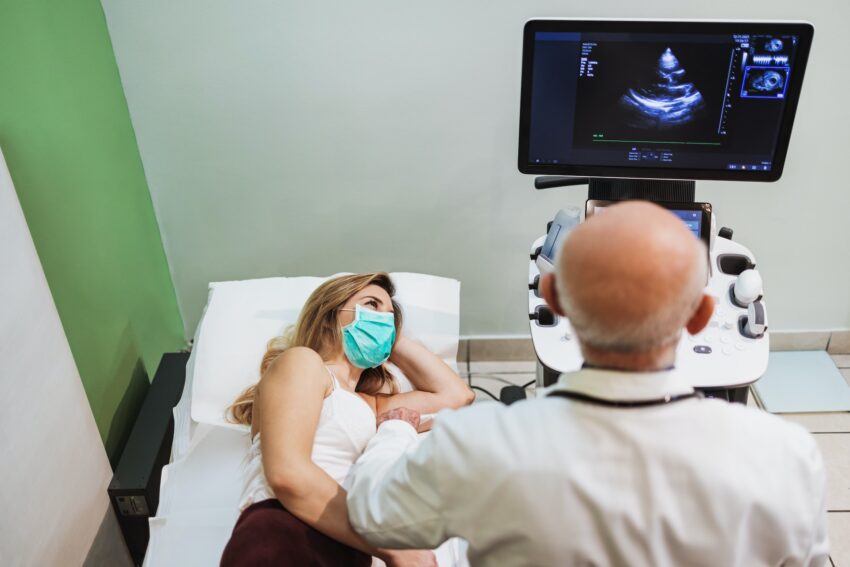
As part of the prenatal care process, healthcare providers use various types of scans to monitor the health and development of the baby. These scans offer valuable insights into the growing fetus and assist in identifying any potential concerns. This article will explore the different types of scans commonly used in pregnancy.
Transabdominal Ultrasound
The transabdominal ultrasound is the most common type of scan during pregnancy. It involves applying a gel on the pregnant person’s abdomen and using a handheld device called a transducer to emit sound waves into the uterus. These sound waves bounce back, creating images of the baby on a monitor. Transabdominal ultrasounds provide an overall view of the baby’s size, position, and development.
Transvaginal Ultrasound
This type of scan (less commonly used) involves inserting a small, lubricated probe into the vagina, providing a closer and more detailed view of the uterus and early pregnancy. In early pregnancy, transvaginal ultrasounds might be used to confirm viability, determine gestational age, and detect potential abnormalities.
Dating Scan
A dating scan is typically performed around 8-14 weeks of pregnancy. This scan measures the baby’s size and the gestational sac, enabling healthcare providers to estimate the due date more accurately. The dating scan is an important milestone that helps establish a timeline for subsequent scans and ensures appropriate monitoring throughout the pregnancy. You can attend pregnancy scans in London to help date your baby.
Nuchal Translucency (NT) Scan
. This scan measures the thickness of the fluid at the back of the baby’s neck, known as the nuchal translucency, and is done around 11-14 weeks. This scan assesses the risk of Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities. The results, combined with maternal age and blood test results, provide a more comprehensive evaluation of the baby’s risk profile.
Anatomy Scan
The anatomy or anomaly scan is conducted around 18-22 weeks of pregnancy. This detailed scan examines the baby’s anatomy and development, assessing various organs, bones, and structures. It helps identify potential abnormalities or structural defects, allowing for early detection and appropriate medical management if required.
Growth Scan
A growth scan is performed at different stages of pregnancy to evaluate the baby’s growth and estimate its weight. It is used to ensure that the baby is growing at the expected rate. Growth scans are particularly important for high-risk pregnancies or if there are concerns about fetal growth.
Doppler Scan
A Doppler scan uses ultrasound technology to assess blood flow in the baby’s umbilical cord and placenta – providing information on oxygen and nutrient supply. Doppler scans are commonly used in high-risk pregnancies or if there are concerns about fetal well-being.
3D/4D Scan
3D and 4D scans, unlike traditional ultrasound scans, provide a more detailed and lifelike view of the baby. These scans use advanced imaging techniques to create three-dimensional images or real-time video footage of the baby’s face and body. While 3D scans offer still images, 4D scans add the dimension of time, allowing parents to see their baby’s movements in real time. These scans provide a unique bonding experience and create lasting memories.
Each type of scan serves a specific purpose in monitoring the health and development of the baby throughout pregnancy. From confirming pregnancy and establishing the due date to assessing fetal anatomy and growth, these scans offer vital information that guides medical care and ensures the well-being of both the baby and the expectant parents. By understanding the different types of scans, expectant parents can actively participate in their prenatal care and nurture their growing bond with their unborn child.